The Israel-Gaza conflict is once again in the international spotlight, as the Palestinian militant group Hamas launched an unprecedented attack on Israel. The situation is complex, and it’s important to grasp the key players, locations, and context to make sense of this ongoing conflict. In this article, we will delve into the roots of the conflict, the nature of Hamas, the current events in the Gaza Strip, and the humanitarian crisis that has arisen.

Israel is at war with Hamas. Everything you need to know
Relief groups are calling for urgently needed humanitarian aid to enter the Gaza Strip, which the United Nations says is being “strangled” by Israel’s tight siege. Tens of thousands of Palestinians are in need of food, water, fuel and medical supplies as resources dwindle and the Israeli military pounds the enclave.
The Israeli military late last week told all civilians in Gaza City to evacuate “southwards” as it maintains its bombardment of the coastal enclave in response to last weekend’s Hamas attacks that killed more than 1,400 people in Israel. Concerns are also growing that further escalation risks drawing Israel’s regional foes into the long-running conflict.
Diplomatic efforts are intensifying. Egypt is facing pressure to open a humanitarian corridor through the Rafah crossing between Egypt and Gaza, the only viable outlet to get people out of the enclave and supplies into it. Meanwhile, US Secretary of State Antony Blinken is on a frantic shuttle mission around the region to ensure the war does not escalate further.
Israel’s assault has killed at least 2,750 people and injured more than 9,700 in Gaza, Palestinian officials say.
Here’s what we know so far.
What is Hamas?
Hamas is an Islamist organization with a military wing that emerging in 1987 out of the Muslim Brotherhood, a Sunni Islamist group that was founded in the late 1920s in Egypt.
The group, like most Palestinian factions and political parties, insists that Israel is an occupying power and that it is trying to liberate the Palestinian territories. It considers Israel an illegitimate state and has called for its downfall.
Unlike some other Palestinian factions, Hamas refuses to engage with Israel. In 1993, it opposed the Oslo Accords, a peace pact between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) that saw the PLO give up armed resistance against Israel in return for promises of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel. The Accords also established the Palestinian Authority (PA) in the Israeli-occupied West Bank.
Hamas presents itself as an alternative to the PA, which has recognized Israel and has engaged in multiple failed peace initiatives with it. The PA, whose credibility among Palestinians has suffered over the years, is today led by President Mahmoud Abbas.
It has over the years claimed many attacks on Israel and has been designated as a terrorist organization by the United States, the European Union and Israel. Israel accuses its archenemy Iran of backing the group.
Hamas rules Gaza, the small strip of land bordering Israel and Egypt that has changed hands several times over the past 70 years. The vast majority of its population are descendants of refugees who were either expelled or forced to flee their homes in 1948 in what is now Israel.
Hamas’s history is entangled with resistance to Israeli occupation and a desire to establish an independent Palestinian state. However, their approach, which includes launching rockets into Israel, has often been criticized as it targets civilians. This has led Israel to respond with airstrikes to counter the attacks. These clashes between Hamas and Israel have occurred intermittently, causing death and destruction on both sides.
Furthermore, Hamas is classified as a terrorist organization by Israel, the United States, the European Union, the UK, and several other countries. Its funding and support come from multiple sources, notably Iran, which provides weapons, training, and financial assistance.
Understanding Palestine and Its Complex History
To comprehend the Israel-Gaza conflict, one must appreciate the broader context of the Israeli-Palestinian dispute. The land historically known as Palestine has been a central element in this complex narrative. The West Bank and Gaza, both Palestinian territories, along with East Jerusalem, were part of a region known as Palestine for centuries. This land has deep historical and cultural significance for both Palestinians and Israelis.
Israel declared statehood in 1948, marking a turning point in the region’s history. However, the land is still referred to as Palestine by those who do not recognize Israel’s right to exist. Palestinians, too, use the name Palestine as an umbrella term encompassing the West Bank, Gaza, and East Jerusalem.
Why Israel and Hamas are Fighting
The conflict between Israel and Hamas is characterized by ongoing tension, punctuated by sudden escalations in violence. The recent attack on Israel, initiated by Hamas, was notably without warning. Thousands of rockets were launched into Israel, and dozens of fighters breached the border, infiltrating Israeli communities, causing civilian casualties, and taking hostages. In response, Israel initiated airstrikes, claiming to target militant sites in Gaza.
This attack, however, is not just another chapter in the long-standing conflict. It is, by many accounts, the most ambitious operation Hamas has ever launched from Gaza. Moreover, it represents the most significant cross-border attack Israel has faced in more than a generation. The audacious nature of the attack raises questions about the effectiveness of Israel’s intelligence agencies, given their extensive resources and monitoring capabilities. Despite Israel’s robust intelligence infrastructure and continuous surveillance, the breach was not anticipated or prevented.
What happened?
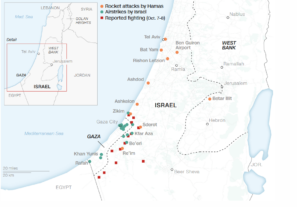
Militants from Gaza fired thousands of rockets towards Israeli towns on October 7, before breaking through the heavily fortified border fence with Israel and sending militants deep into Israeli territory. There, Hamas gunmen killed more than 1,400 people, including civilians and soldiers, and took 199 hostages, according to Israeli authorities.
The attacks were unprecedented in tactics and scale as Israel has not faced its adversaries in street battles on its own territory since the 1948 Arab-Israeli war. It has also never faced a terror attack of this magnitude that has taken the lives of so many civilians. While Hamas has kidnapped Israelis before, it has never before taken dozens of hostages at once, including children and the elderly.
Hamas called the operation “Al-Aqsa Storm” and said that it was a response to what it described as Israeli attacks on women, the desecration of the al-Aqsa mosque in Jerusalem and the ongoing siege of Gaza.
How has Israel responded?
In response to the attack, Israel has declared war and launched “Operation Swords of Iron,” striking what it says are Hamas and Islamic Jihad targets in Gaza. It has also blocked supply lines of basic necessities to the Gaza population, including fuel and water.
Between October 7 and 12, Israel dropped 6,000 bombs on the densely inhabited territory – that’s equivalent to the total number of airstrikes on Gaza during the entire 2014 Gaza-Israel conflict, which lasted 50 days.
The IDF has told civilians in Gaza to leave their residential areas immediately for their safety, but some say there is nowhere safe to go. All crossings out of Gaza have been shut.
Complicating Israel’s response are the hostages that Hamas is holding. Hamas has said that a number of hostages have been killed by Israeli bombings on the enclave. Israeli hasn’t confirmed or denied the claim.
Israel has ordered a “complete siege” on Gaza, blocking delivery of electricity, food, fuel and water until the hostages are freed.
Israel’s military told the 1.1 million people in northern Gaza to evacuate their homes immediately, suggesting that a ground invasion was imminent.
What’s the situation in Gaza now?
A humanitarian crisis in Gaza is rapidly spiraling amid warnings that people are at risk of starvation as Israel tightens its chokehold on the territory.
The Gaza Strip is one of most densely populated places on earth, with some 2 million people crammed in 140-square-mile territory. The enclave lies on Egypt’s western border and has been under blockade since Hamas seized control in 2007.
The Israeli air, naval and land blockade on the territory, as well as the Egyptian land blockade, continue today.
The enclave’s only power station stopped working last week. Hospitals are expected to run out of fuel, with the International Committee of the Red Cross warning that they “risk turning into morgues” as they lose power. Airstrikes have hit at least 88 education facilities and killed at least 12 UN personnel, according to the UN.
Human rights groups have warned of possible war crimes being committed in Gaza. Amnesty International has urged Israel to “immediately” lift its blockade on the enclave, saying the “collective punishment” of civilians for Hamas’ terrorism amounts to a war crime.
Since Israel shut its two crossings with Gaza, the only corridor through which Palestinians or aid can pass in and out of the territory is the Rafah Crossing, which connects the south of the enclave to Egypt. That crossing remains shut, but the US has been working to open it. International aid has arrived in Egypt is being held up at the border.
Hamas has called on Gazans not to leave their homes, accusing Israel of engaging in “psychological warfare” by calling on Palestinians to evacuate to the south. “Displacement and exile are not for us,” Hamas said.
How did the two sides get here?
Tensions between Israelis and the Palestinians have existed since before Israel’s founding in 1948. Thousands of people on both sides have been killed and many more injured over decades.
Violence has been particularly acute this year. The number of Palestinians – militants and civilians – killed in the occupied West Bank by Israeli forces since the year began is the highest in nearly two decades. The same is true of Israelis and foreigners – most of them civilians – killed in Palestinian attacks.
Israel captured Gaza from Egypt in the 1967 war, then withdrew its troops and settlers in 2005. The territory, home to some 2 million Palestinians, fell under Hamas’ control in 2007 after a brief civil war with Fatah, a rival Palestinian faction that is the backbone of the Palestinian Authority.
After Hamas seized control, Israel and Egypt imposed a strict siege on the territory, which is ongoing. Israel also maintains an air and naval blockade on Gaza.
Human Rights Watch has called the territory an “open-air prison.” More than half of its population lives in poverty and is food insecure, and nearly 80% of its population relies on humanitarian assistance.
Hamas and Israel have fought several wars. Before the operation on October 7, the last war between the two was in 2021, which lasted for 11 days and killed at least 250 people in Gaza and 13 in Israel.
Saturday’s assault occurred 50 years almost to the day since the 1973 war, when Israel’s Arab neighbors launched a surprise attack on Israel on Yom Kippur, the holiest day in the Jewish calendar, on October 6, 1973.
What happens next?
Israel is on a war footing and has amassed more than 300,000 reservists along the Gaza border for a potential ground operation. It has said that it will exact a heavy price on Hamas for its attack and plans to retrieve Israeli hostages from the territory.
Israel has dealt with hostage situations before, but never at this scale. In the past, militants have mostly demanded the release of prisoners held in Israeli jails in exchange for captured Israelis. In 2011, Israel released more than 1,000 Palestinian prisoners in exchange for one kidnapped soldier.
Hamas has said that it is ready “for all options, including a war and an escalation on all levels,” including a ground invasion.
Could this lead to a wider regional conflict?
US National Security Adviser Jake Sullivan on Sunday warned of the risk of a wider regional conflict in the Middle East.
Blinken has meanwhile traveled to Israel, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Egypt and Bahrain, in an attempt to prevent escalation.
The White House nonetheless Monday announced that US President Joe Biden is scrapping a planned trip to Colorado just hours before he was set to depart, so he can instead hold meetings with his national security team as the conflict heats up.
Israel has also invited Biden to the country for talks with Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, and both sides were considering the visit, Biden has issued a stark warning to Iran to “be careful” around its actions in the region.
While a direct link between Iran and the attack has not been established, both Israel and the US say that the Islamic Republic is the primary backer of the Palestinian group.
Iran has denied involvement in the attack and warned Israel against targeting its allies in Lebanon. Iran-backed Hezbollah, which the US and Israel consider a terrorist organization, has engaged in an exchange of fire with Israel since the Gaza war began. Those altercations have however been confined to the two countries’ border areas.
“Lebanon’s security is Iran’s security,” Iranian Foreign Minister Hossein Amirabdollahian said last week, adding that it is “probable” that a new front would open against Israel if it continued “war crimes” in Gaza.
The US has ordered two carrier strike groups to the eastern Mediterranean Sea and is sending more fighter jets to the region to deter potential Iranian potential aggression or an expansion of the fighting beyond Israel’s borders.
Israel has said it’s ready to fight a war on multiple fronts.
The Gaza Strip: A War-Torn Territory
The Gaza Strip, a slender piece of land measuring 41 kilometers long and 10 kilometers wide, is located between Israel, Egypt, and the Mediterranean Sea. It houses approximately 2.3 million people, resulting in one of the highest population densities globally. However, the Gaza Strip is far from an idyllic location; it has long been a focal point of conflict.
Israel controls the airspace over Gaza and its shoreline, governing who and what can enter or exit through border crossings. Egypt, too, plays a significant role in controlling movement across its border with Gaza. The tight restrictions have created a challenging environment for Gazans, as around 80% of the population relies on international aid, with nearly a million individuals dependent on daily food assistance to survive.
Humanitarian Concerns in Gaza
As the conflict intensifies, humanitarian concerns mount in the Gaza Strip. Relief organizations are sounding alarm bells, urging the delivery of essential aid to the region. The United Nations has characterized the situation as the Gaza Strip being “strangled” by Israel’s tight siege. Thousands of Palestinians are in dire need of food, water, fuel, and medical supplies, as essential resources dwindle while the Israeli military continues its bombardment.
Last week, the Israeli military instructed all civilians in Gaza City to evacuate “southwards,” further complicating the humanitarian crisis. There is growing apprehension that further escalation could draw Israel’s regional adversaries into the long-running conflict. Efforts are intensifying on the diplomatic front, with Egypt under pressure to open a humanitarian corridor through the Rafah crossing, providing an outlet for supplies and people to enter and leave the enclave.
Though a CNN staffer at the Rafah border crossing witnessed UN fuel trucks entering Gaza, the overall delivery of humanitarian aid remains limited. Meanwhile, the U.S. Secretary of State, Antony Blinken, is embarking on a shuttle mission across the region to prevent further escalation of the war.
The Recent Events in Gaza and Israel
The recent conflict saw militants from Gaza launching thousands of rockets into Israeli towns. This attack was accompanied by a coordinated breach of the heavily fortified border fence with Israel. These developments led to direct confrontations between Hamas gunmen and Israeli civilians and soldiers. This operation, named “Al-Aqsa Storm” by Hamas, was an unprecedented escalation in tactics and scale.
Israel’s response to this attack was swift and decisive. It declared a state of war and launched “Operation Swords of Iron,” targeting what it claimed were Hamas and Islamic Jihad positions in Gaza. In addition to these military operations, Israel imposed strict blockades on supply lines, depriving the Gaza population of basic necessities, including fuel and water.
The Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) have urged civilians in Gaza to leave their residential areas for their safety. However, the civilians have limited options for escape, as all crossings out of Gaza have been sealed. The complexity of the situation is further exacerbated by the issue of hostages held by Hamas. There have been claims that some hostages were killed in Israeli bombings, although this remains unconfirmed.
As a response to these developments, Israel has initiated a complete siege on Gaza. Essential supplies such as electricity, food, fuel, and water are being blocked until the hostages are released. On a more ominous note, Israel’s military advised the 1.1 million people in northern Gaza to evacuate their homes immediately, suggesting the possibility of an imminent ground invasion.
The Dire Humanitarian Crisis
Gaza, with its dense population and limited space, is now experiencing a rapidly escalating humanitarian crisis. The situation is dire, with fears of starvation, as Israel tightens its grip on the territory. Gaza’s status as an open-air prison is compounded by the Israeli air, naval, and land blockade that has been in place since Hamas took control in 2007. The sole power station in the region ceased to function, and hospitals are on the brink of losing power, risking the transformation of these medical facilities into morgues.
International organizations and human rights groups have raised concerns about possible war crimes in Gaza. Amnesty International has called on Israel to “immediately” lift its blockade, arguing that the collective punishment of civilians for Hamas’ actions amounts to a war crime. Gaza’s two crossings to the outside world are effectively sealed, except for the Rafah Crossing, which connects the southern part of Gaza to Egypt. However, this crucial passage remains shut, despite international efforts to open it. Aid shipments are being held up at the border, exacerbating the crisis.
What Lies Ahead?
As tensions escalate, Israel is on high alert, amassing more than 300,000 reservists along the Gaza border, indicating the potential for a ground operation. The situation is further complicated by the issue of hostages held by Hamas, a situation Israel has dealt with before, albeit not on this scale. In the past, hostage situations were often linked to the release of Palestinian prisoners held in Israeli jails.
Hamas has declared its readiness for any potential scenarios, including war and escalation on various fronts, indicating the gravity of the situation. The international community is deeply concerned, with U.S. National Security Adviser Jake Sullivan warning of the risk of a broader regional conflict in the Middle East. The U.S. Secretary of State, Antony Blinken, has embarked on an extensive diplomatic mission to prevent further escalation.
The White House’s decision to cancel U.S. President Joe Biden’s planned trip and his stern warning to Iran further underscore the potential for a wider regional crisis. While a direct connection between Iran and the attack has not been confirmed, both Israel and the U.S. identify Iran as Hamas’ primary supporter. These developments have raised concerns over possible Iranian involvement, and the U.S. has deployed military assets to deter potential aggression from Iran or the expansion of the conflict beyond Israel’s borders.
Israel, for its part, has signaled readiness to confront a multi-front war, underlining the gravity of the situation and the pressing need for international intervention.
In conclusion, the ongoing conflict between Israel and Hamas in the Gaza Strip has deep historical roots, complex geopolitical dimensions, and significant humanitarian concerns. The international community must continue to strive for diplomatic solutions to mitigate the suffering of civilians and prevent further escalation of violence.
